THE SCALP, A SPECIAL KIND OF SKIN
 The scalp is the part of the skin that covers the skull and develops hair-like pilosity. The scalp extends over the entire skull and follows its shape. In adults, the scalp is 6 mm thick and has a surface area of 600 to 700 cm2. In comparison, 20 cm-long hair represents only 6m2. The visible part of the hair is biologically dead, while the scalp is the living part of the hair. The scalp is continuous, supple and resistant, from the outside in:
The scalp is the part of the skin that covers the skull and develops hair-like pilosity. The scalp extends over the entire skull and follows its shape. In adults, the scalp is 6 mm thick and has a surface area of 600 to 700 cm2. In comparison, 20 cm-long hair represents only 6m2. The visible part of the hair is biologically dead, while the scalp is the living part of the hair. The scalp is continuous, supple and resistant, from the outside in:
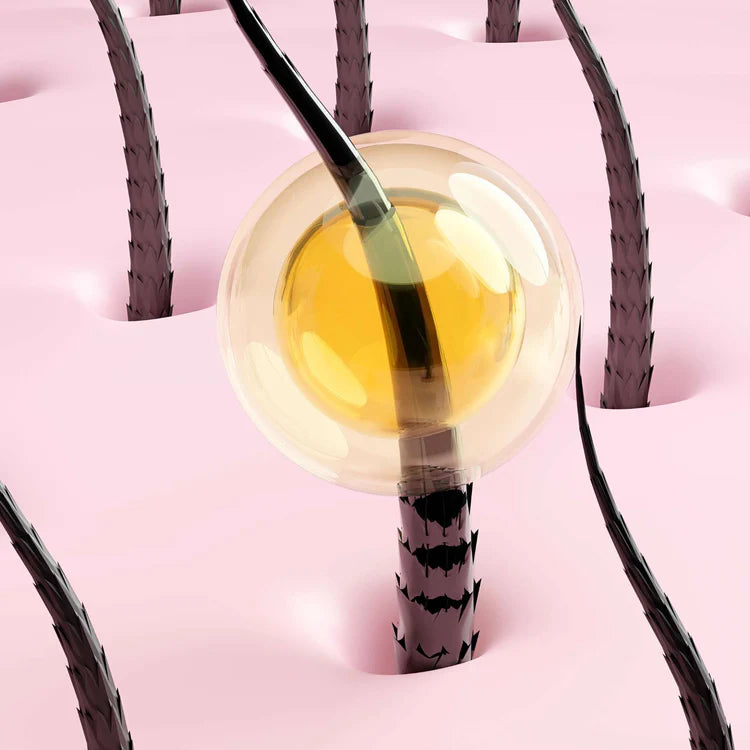
- The skin. The skin is made up of a protective epidermis and a supporting dermis. The dermis is thicker and more vascularized than the dermis of facial skin. The hair root is located in this layer at a depth of around 2.5 mm. It contains numerous blood vessels to allow the hair root to develop.
- Subcutaneous tissue. This is a fatty tissue equivalent to the skin's hypodermis. The hair bulb is located in this layer at a depth of around 3.5 cm.
- Galea. This is the tissue that covers the skull and holds the muscular tissues together.
THE SPECIFICITIES OF THE SCALP
The scalp is a continuation of facial skin, and shares many similarities with it: the presence of an epidermis, a dermis, pores, sebum on the surface, sweat and sebaceous glands, and follicular bulbs for hair. However, the scalp has specific characteristics compared to facial skin. The pH of the scalp is between 4.5 and 5.5. The scalp has an abundance of hair follicles, producing 250 to 300 hairs per cm2 of scalp. The scalp also has more sweat glands, secreting sweat, and sebaceous glands, producing sebum, than facial skin.
The composition of sebum is different on the scalp: there are more free fatty acids than on the skin. Sebum production is in the order of 0.7 to 1g per 24h on the scalp. Sebum is a fluid grease containing lipids (triglycerides), waxes, and fatty acids. The sebaceous glands produce sebum and secrete it to the surface of the scalp. Sebum holds the epidermis together, protecting it from UV rays and micro-organisms.
THE SKIN MICROBIOTA OF THE SCALP
The scalp also has its own specific skin microbiota. The scalp is considered a humid zone, i.e. with apocrine glands, high hair density, and a moist, clogged environment. On average, moist sites contain 28% Corynebacterium, 26% Proteobacteria, and 21% Staphylococcus. Scalp sites are dominated by the following micro-organisms: Staphylococci (S. captis, S. epidermidis), Propionibacterium (P.acne, P. granulosum, P. avedum), Malassezia (causing dandruff).
ROLES OF THE SCALP
The scalp has two important roles. Firstly, the scalp is the birthplace of hair follicles. Keratinocytes in the bulb manufacture the components that enable hair growth, thanks to its connections with blood vessels, and particularly with nutrients. The scalp is also a protective barrier, like the epidermis on our face. The scalp is both a physical barrier, to protect against dehydration, but also a protection against microorganisms, and a thermal insulator.
SCALP PROBLEMS
The scalp is similar to the skin, so the use of skincare products is essential. It's important to understand the scalp and its problems, in order to use scalp-specific skincare products. A healthy, balanced scalp is a healthy scalp, and will result in beautiful, vital hair. So it's worth using products to care for the scalp's cutaneous microbiota, in particular to reduce the proliferation and eliminate fungus and dandruff, while respecting the skin's flora. The main problems encountered in the scalp are:
SENSITIVITY
Sensitivity refers to irritation, itching, dryness, dandruff, and tightness of the scalp. This can be due to stress, pollution, diet, sun exposure, or aggressive skincare products. To combat and care for a sensitive scalp, you need to let the scalp breathe and moisturize it to promote cell renewal.
ALOPECIA
Alopecia is defined as hair loss. It can be hormonal, genetic or medical in origin, mainly in men but also in women. To combat hair loss, we recommend the use of products that stimulate the keratinocytes of the hair bulbs in the scalp.
DANDRUFF
This is a scalp dysfunction caused by disruption of the cohesion between corneocytes. Dandruff can be either oily (voluminous clusters) or dry (small, white flakes): it also causes discomfort and itching of the scalp. Dry dandruff is caused by the scalp's epidermis renewing itself too quickly, while oily dandruff is caused by bacteria or fungi feeding on the scalp's sebum. The main cause of dandruff is Malassezia, influenced by hormones, the seasons, stress and excessive use of hair-type products. To care for this type of scalp, you need to use fungicidal active ingredients or active ingredients that rebalance the scalp microbiota.
DERMATOSIS
There are a number of dermatoses affecting the scalp. Parasitic dermatoses, such as lice, are widespread. Fungal dermatoses are caused by the growth of fungi. The most common of these are desquamative dermatoses. These include hyperseborrhea, due to overproduction of sebum, and hyposeborrhea, due to underproduction. Dermatitis or psoriasis, which develop on the skin, can also be present on the scalp.
THE SCALP, A FAST-GROWING MARKET

The global hair and scalp market is expected to reach $134 billion by 2028. Today, 50% of products targeting the scalp are in the shampoo category. However, between 2018 and 2021, 20% growth has been observed in sales of hair care products (excluding shampoo) targeting the scalp. Sales of scalp care products in liquid, serum, or scrub format doubled between 2018 and 2021. Hair care products targeting the scalp claim the following benefits: hydration, brighter, stronger hair, and combating damaged hair and dandruff.